Numerical Simulations: Crack – Initiations in Rolling Contact Areas of Metro Rails in the Vienna Subway
During periodic track inspection of the Vienna subway a new type of surface damage failure was discovered which in some cases led to total failure of the rail.A thorough macroscopic investigation revealed that any tiny surface cracks develop within the running area of the rail together with and in competition with contact-rolling induced sub-surface shear damage.
Failures of this kind seem to have come into existence with the exchange of softer rails by head-hardened rails fabricated of perlitic steel.
It was found that – under certain conditions - the lifetime of these new rails was drastically reduced.
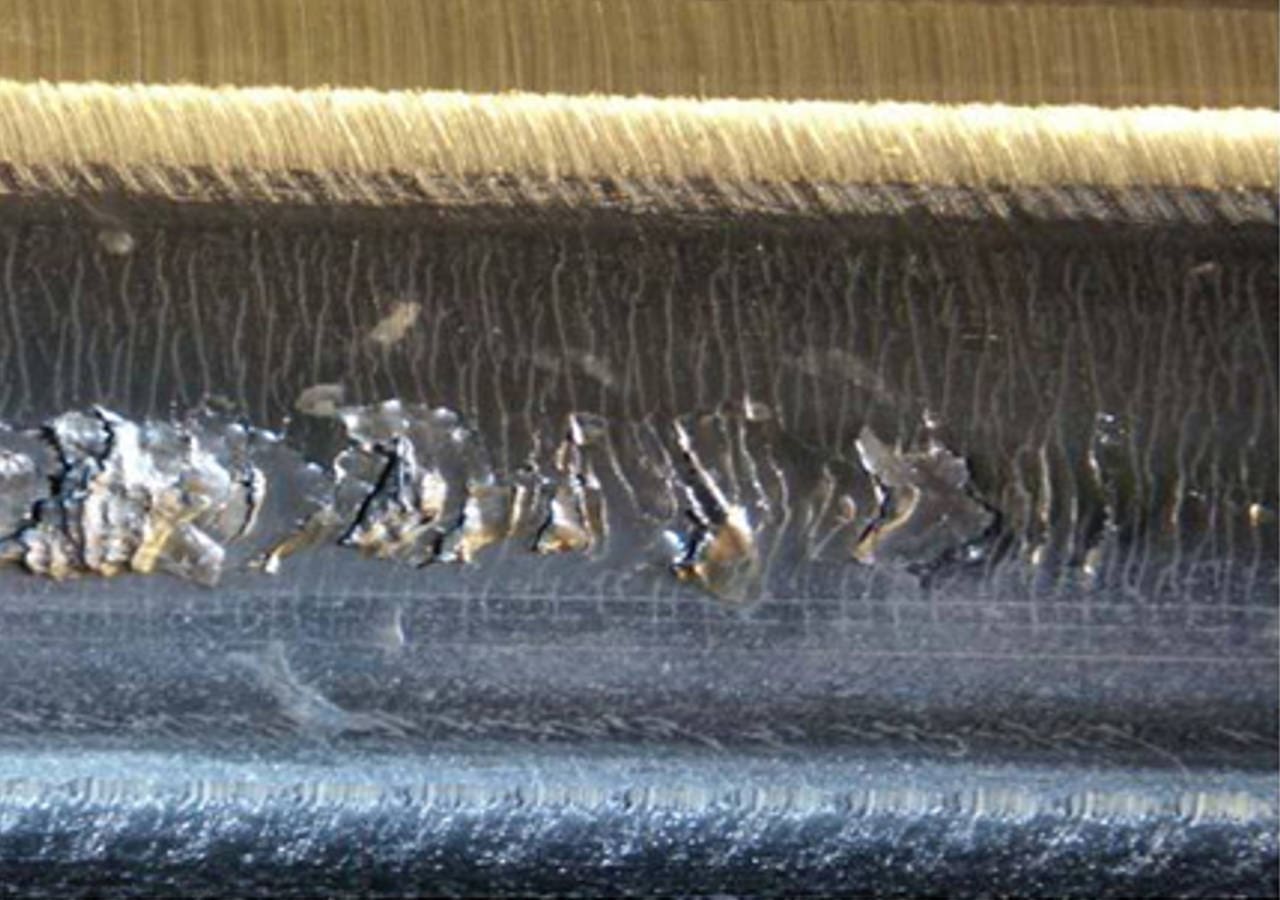

Formation of beam type surface damage in a head- hardened rail.
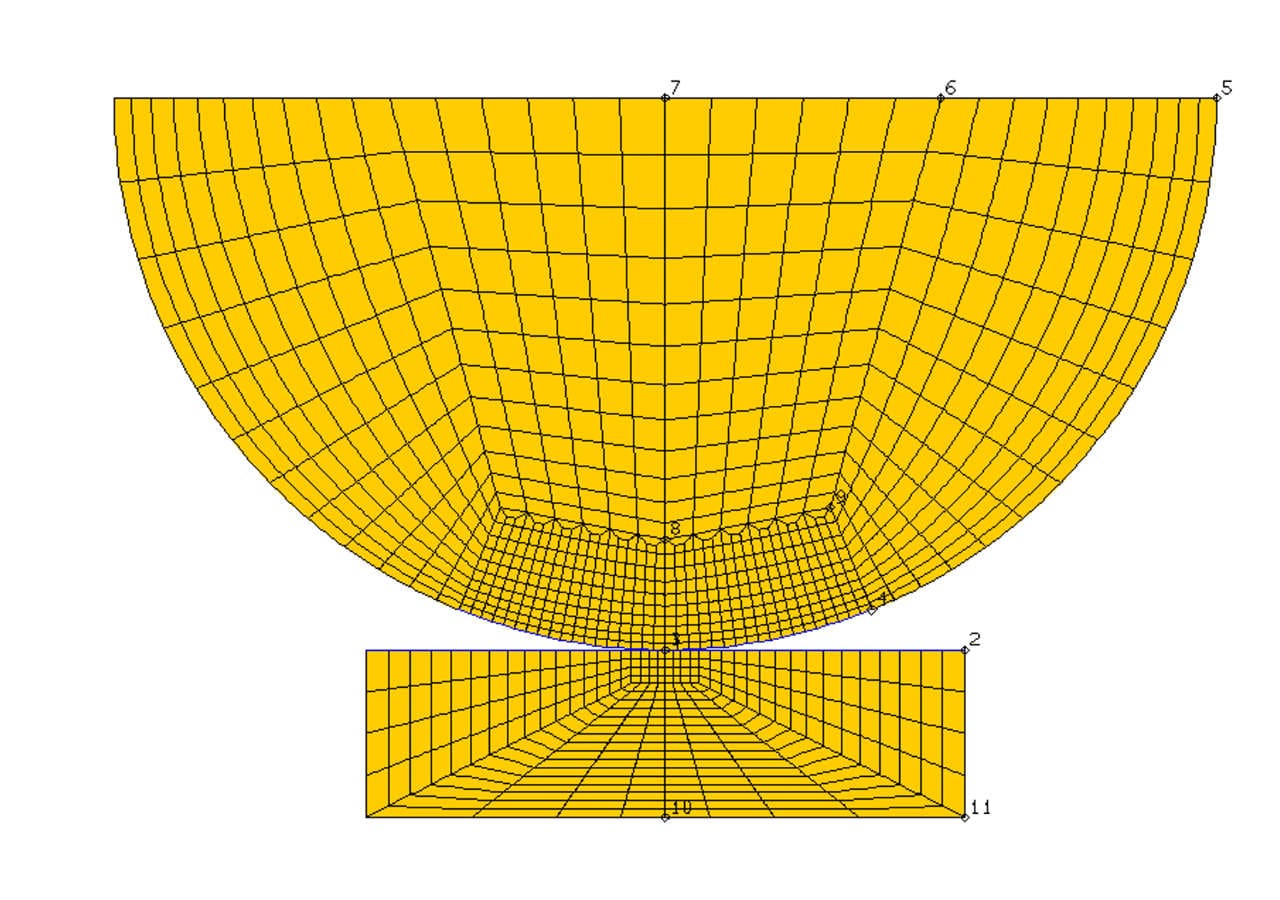
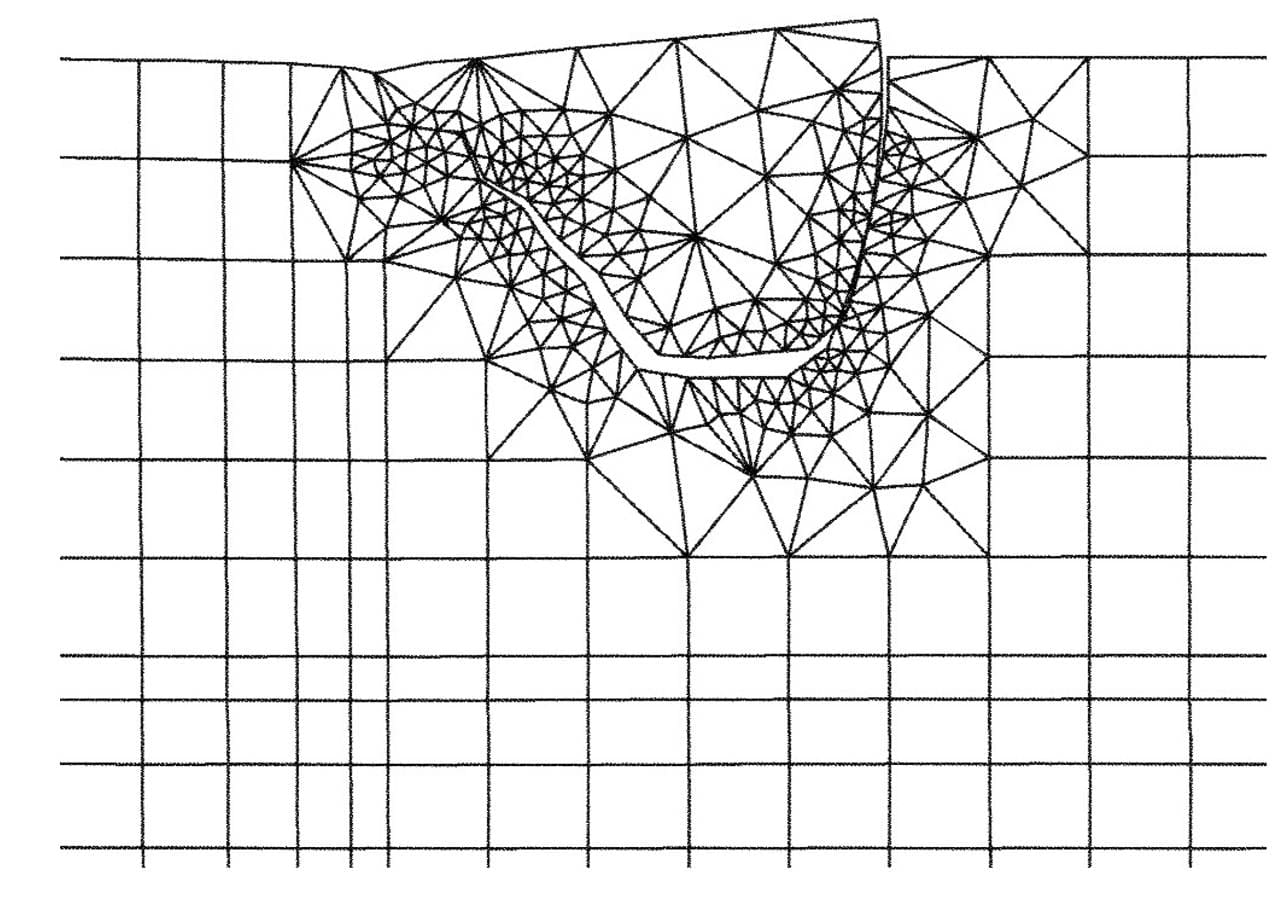
FE-Configuration Wheel/Rail
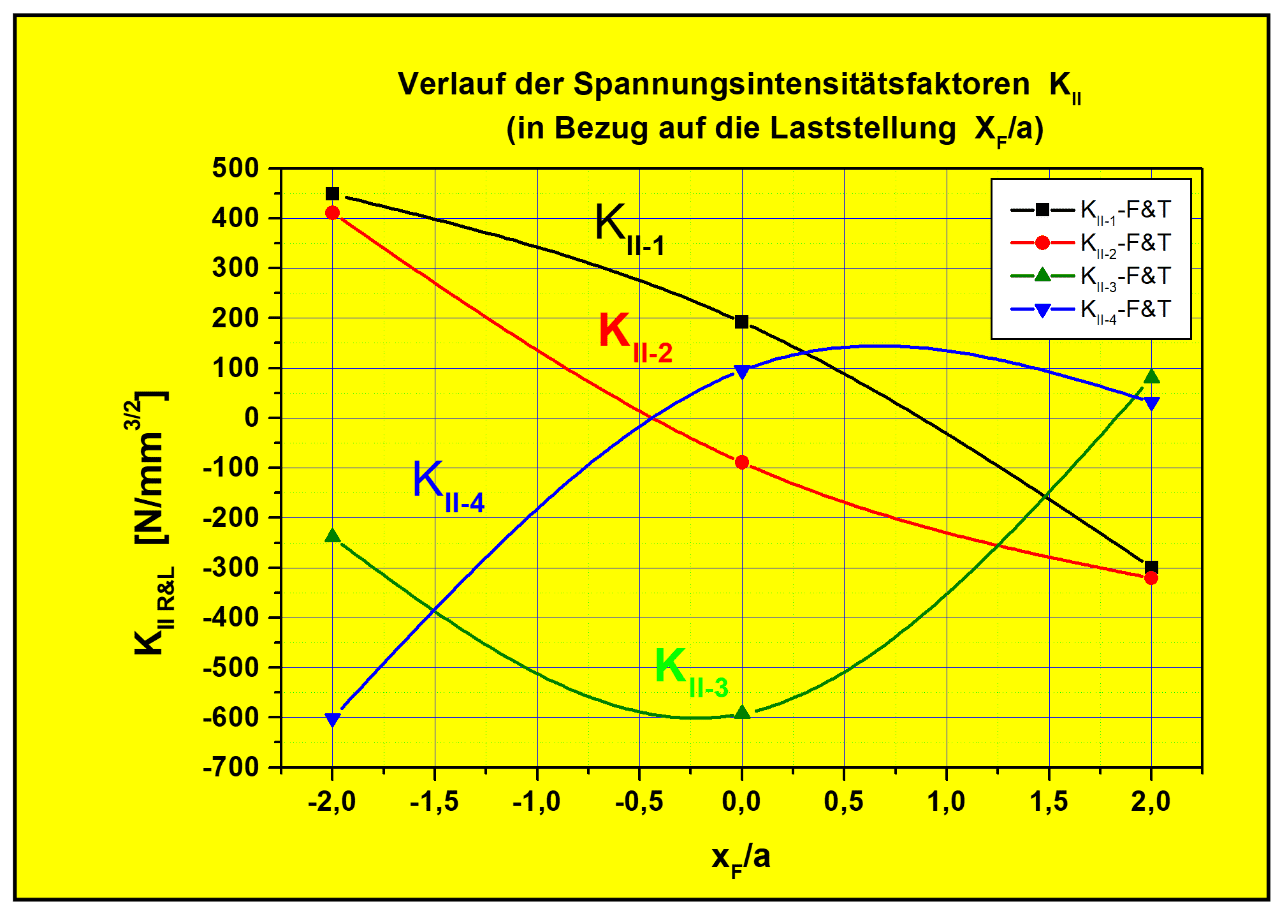
Fluctuation of the Stress Intensity Factor (KII) Distribution in a Rail-Head-Crack -Configuration during the Roll-Over Process
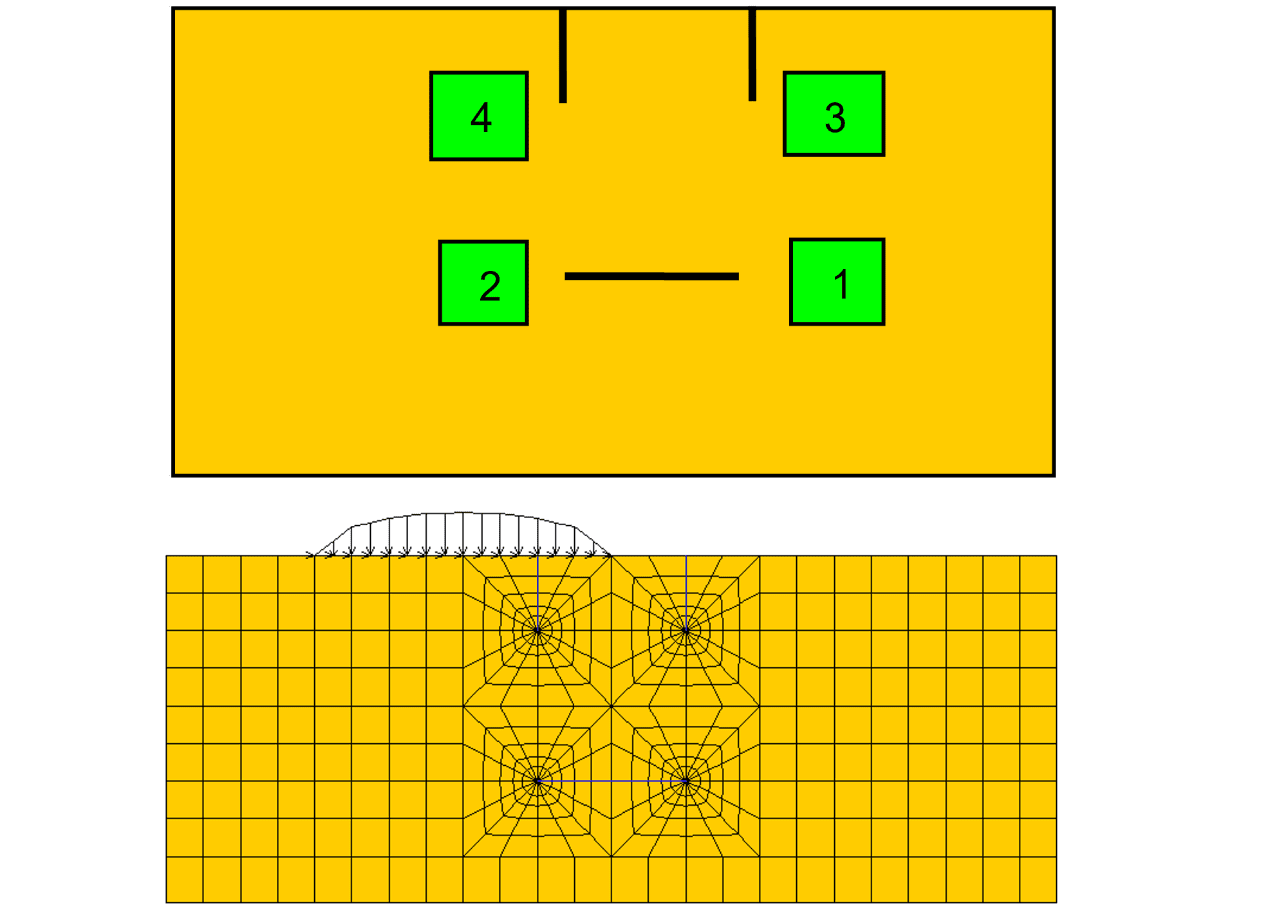
The 'static' fracture mechanics examination is carried out on a cell formation from a micro crack ensemble. The configuration consists of a central shear zone 'representative' crack (1 - 2) and two adjacent surface cracks (3 & 4) as is shown in the FigureCrack-Development- Simulation - Rolling Contact Fatigue
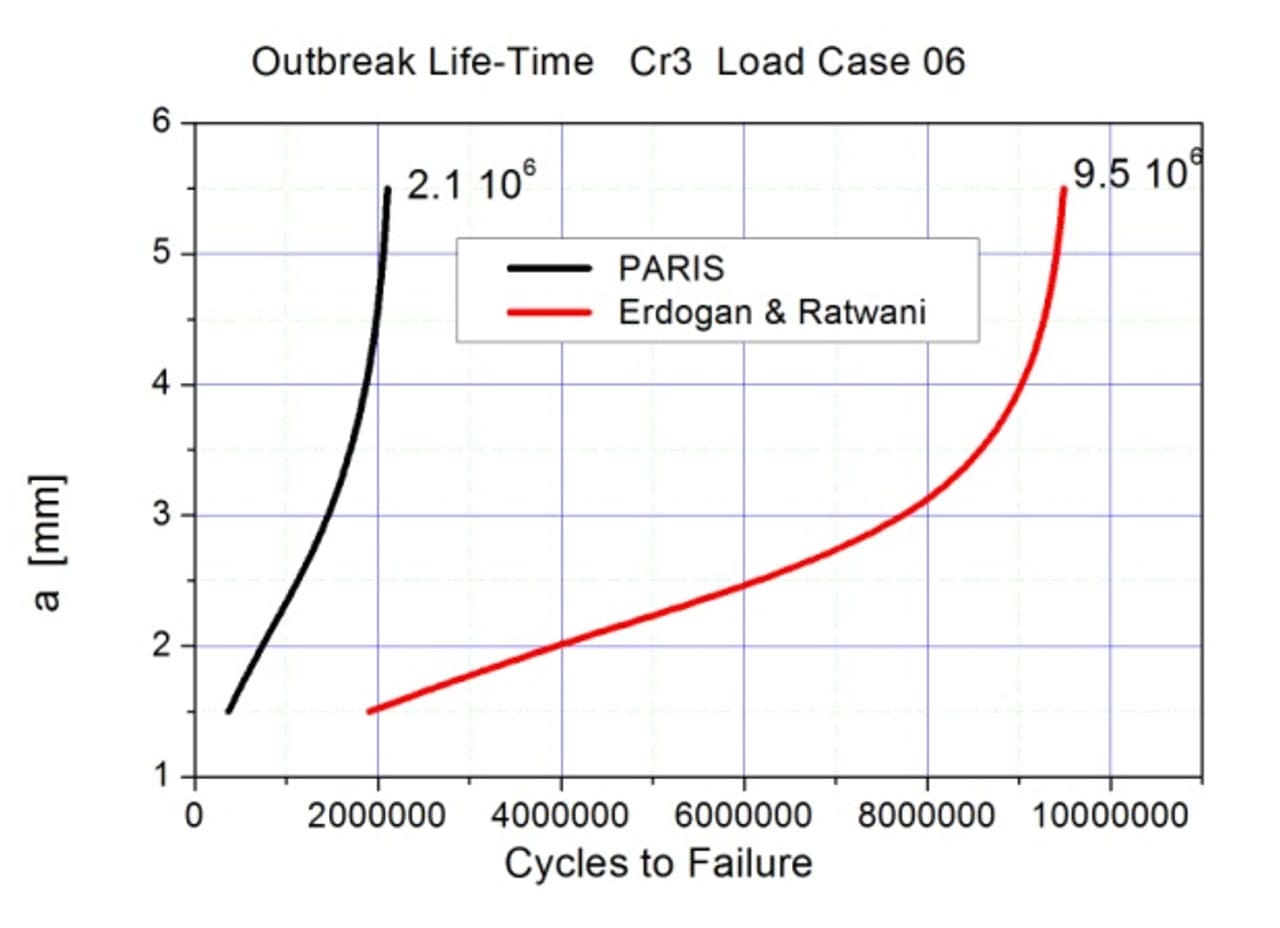
Based on 'special' fatigue fracture mechanics material parameters da/dN vs. ΔK plots according to ASTM-standardized test specimens from R350HT rail steel - a FE investigation was carried out for the stepwise surface crack propagation to simulate the life time up to the full break-out out.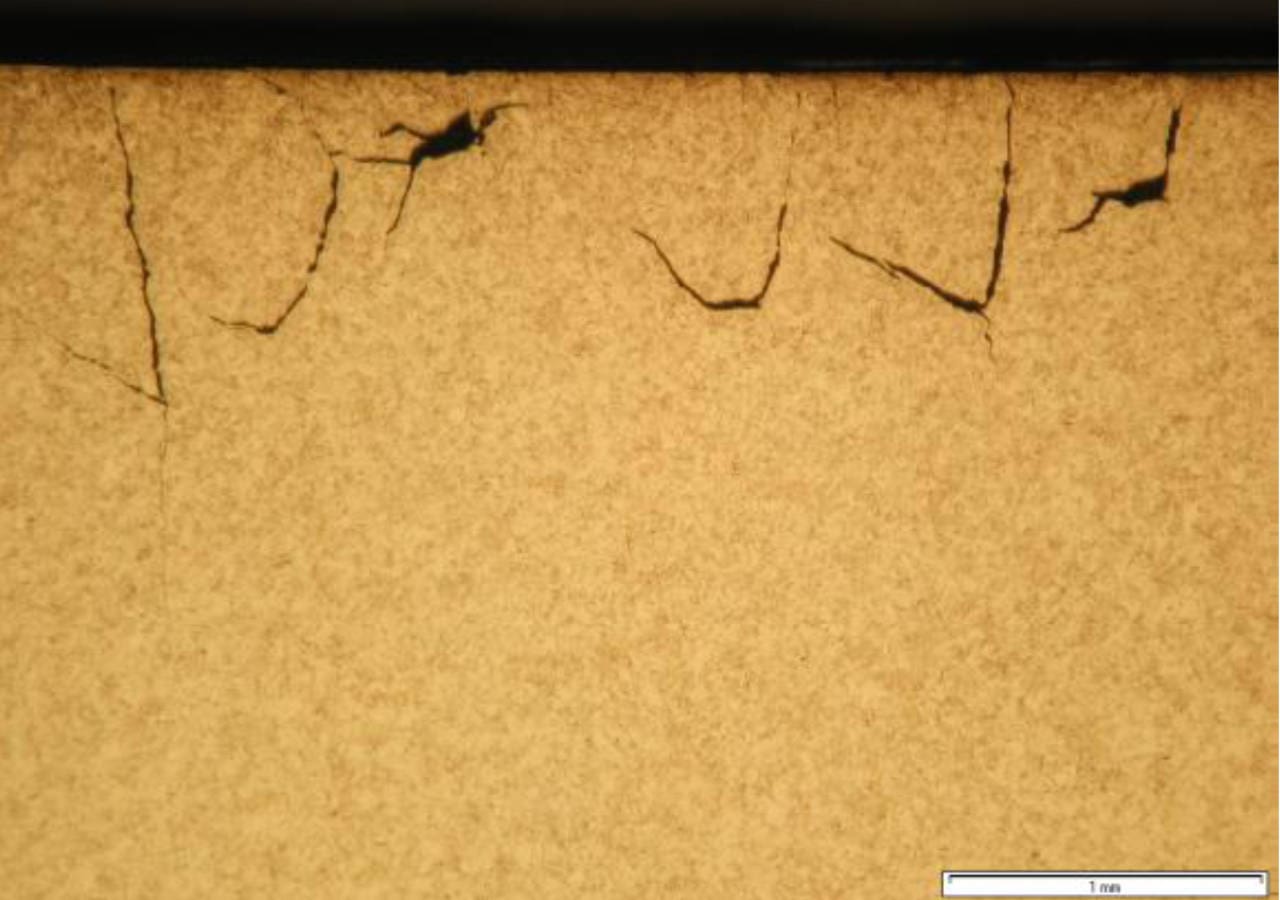
Fatigue crack propagation can be best described by the well-known fracture mechanics based Paris law or its modifications by Erdogan-Ratwani or Forman.
A subway train with 6 carriages yields a bending moment with31 tensile peaks. Regular service in Vienna between 5am and 1am (= 20 service hours) with train intervals of 5 minutes yields 2 489 300 (2.5∙106)tensile maxima per year of service.
The grinding interval either could be aligned on the very conservative Paris-law or on the Erdogan-Ratwani relationship, according to instructions of the authorities.
The grinding interval either could be aligned on the very conservative Paris-law or on the Erdogan-Ratwani relationship, according to instructions of the authorities.
Typical crack extension versus load cycle curves for the two crack propagation concepts show, that the Erdogan-Ratwani concept predicts four and a half longer lifetime as the Paris concept.
Fischmeister E., Linsbauer H., Loibenegger F., Mittermayr P., Oberhauser A.,Rossmanith H.: Schäden an Schienen zufolge Rollkontaktermüdung im Wiener U-Bahnnetz – Teil III. ETR Juni 20010 ,06, 2-8
Linsbauer H., Knasmillner, R., Loibenegger F.: Fracture Mechanics Modeling of Spalling in the Rolling Contact Area of Wheels and Rail during a RCF-Process. Book o Abstracts, The 33rd Danubia Adria Symposium on Advances in Experimenta Mechanics. Portoroz, 2016, 66-67.
Fischmeister E., Linsbauer H., Loibenegger F., Mittermayr P., Oberhauser A.,Rossmanith H.: Schäden an Schienen zufolge Rollkontaktermüdung im Wiener U-Bahnnetz – Teil III. ETR Juni 20010 ,06, 2-8
Linsbauer H., Knasmillner, R., Loibenegger F.: Fracture Mechanics Modeling of Spalling in the Rolling Contact Area of Wheels and Rail during a RCF-Process. Book o Abstracts, The 33rd Danubia Adria Symposium on Advances in Experimenta Mechanics. Portoroz, 2016, 66-67.